Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, playing a crucial role in providing structure to the skin, hair, nails, bones, ligaments, and tendons. It’s often hailed as a cornerstone of anti-aging products and supplements. However, collagen is not a one-size-fits-all protein. There are at least 28 different types of collagen, each serving unique functions and offering distinct benefits. In this post, we’ll delve into the most common types of collagen—Type I, II, III, IV, and V—and explore how they can benefit your health and well-being.
Type I Collagen: The Foundation of Skin, Bones, and More
Type I collagen is the most prevalent form in our bodies. It’s a key component of the skin, bones, teeth, connective tissue, and fibrous cartilage. Supplements containing Type I collagen can promote healthy skin elasticity and hydration, reduce fine lines and wrinkles, and support bone strength. By helping to maintain the density of the dermal matrix, Type I collagen plays a critical role in anti-aging skincare routines.
Type II Collagen: The Joint Guardian
Primarily found in cartilage, Type II collagen is essential for maintaining joint health and flexibility. It helps to cushion joints and reduce friction during movement, which can alleviate pain and stiffness associated with conditions like osteoarthritis. Supplements with Type II collagen are often recommended for individuals seeking to support joint health and mobility.
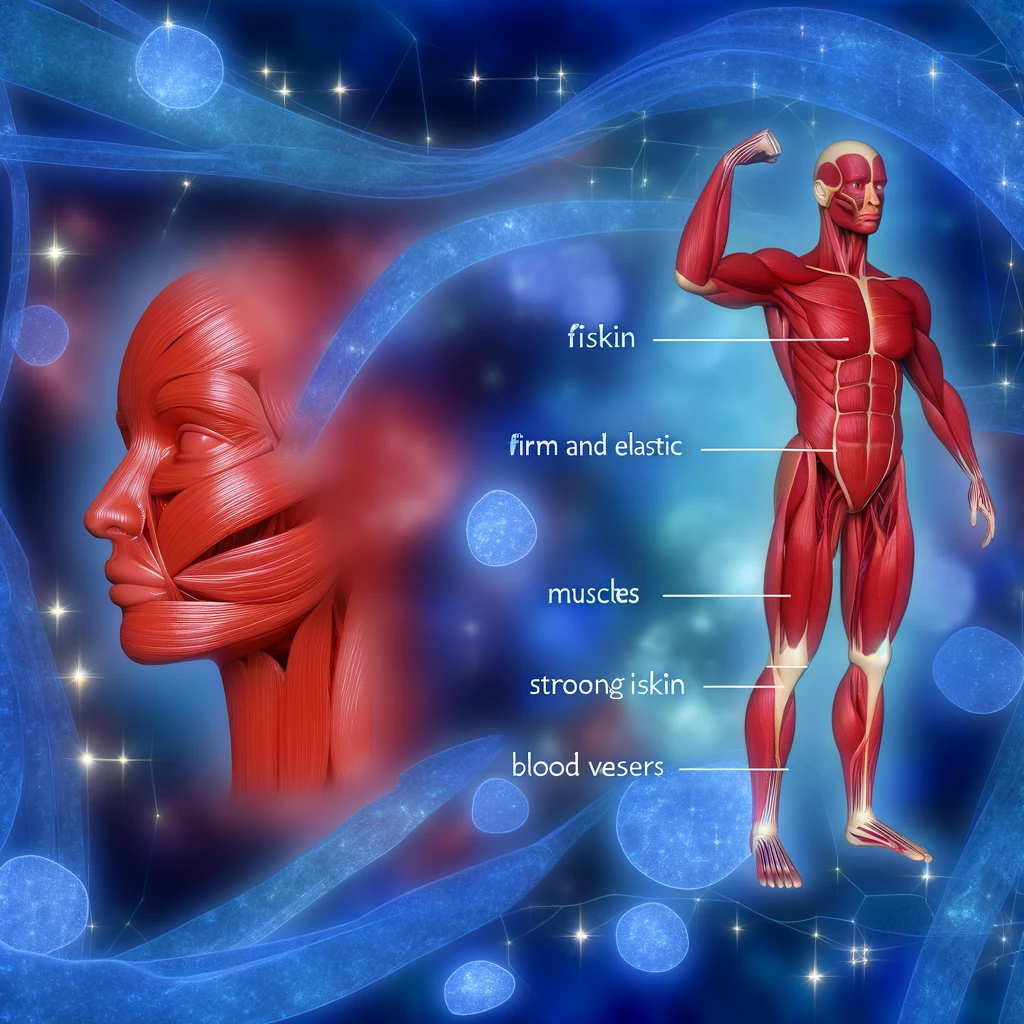
Type III Collagen: The Support Network for Organs and Skin
Type III collagen is found in large quantities in our skin, muscles, and blood vessels. It works in tandem with Type I collagen to support the structure of muscles, organs, and arteries. Type III collagen is critical for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness, and it plays a role in the healing process of wounds.
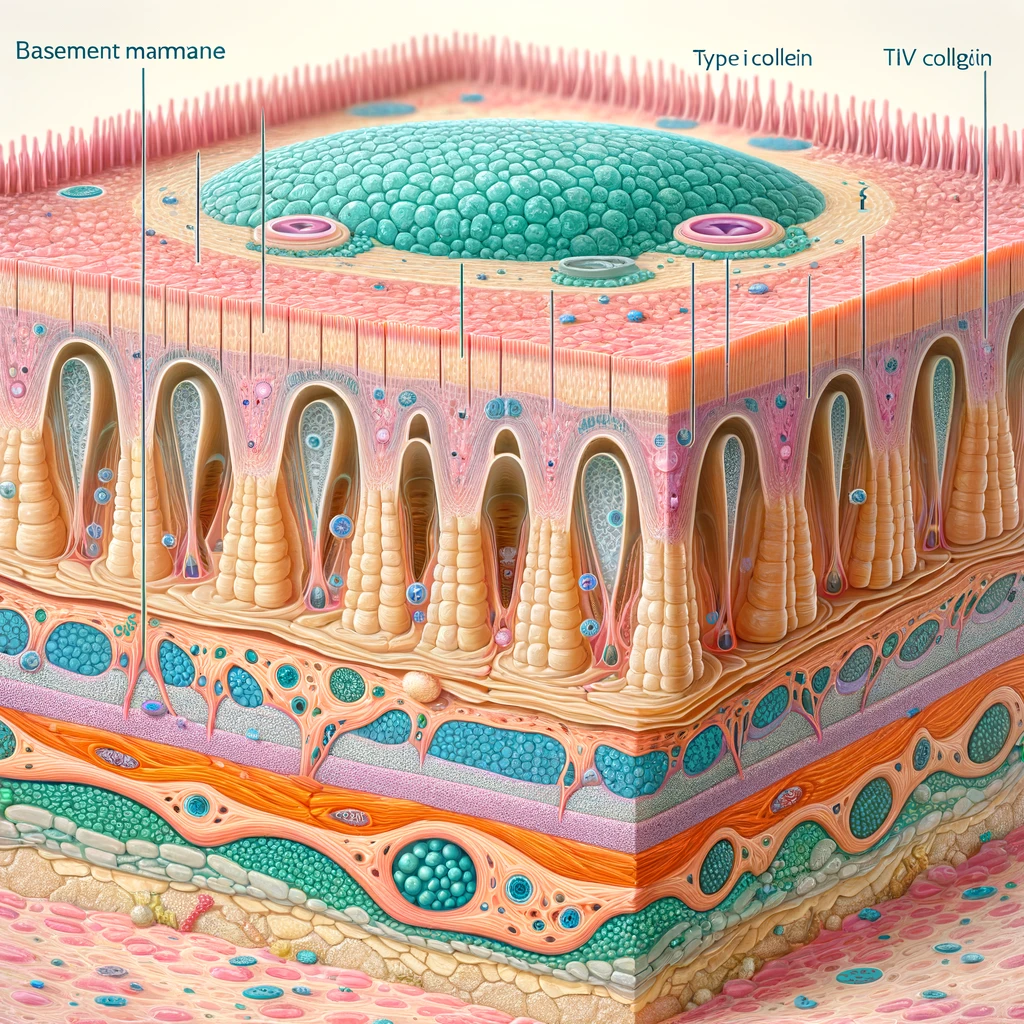
Type IV Collagen: The Basement Membrane Protector
Type IV collagen forms a part of the basement membrane, a layer found in epithelial tissues. It plays a crucial role in filtration, such as in the kidneys, and provides support and protection for layers of the skin, eyes, and various internal organs. By maintaining the integrity of this membrane, Type IV collagen ensures essential substances can pass into and out of tissues and organs efficiently.
Type V Collagen: The Cellular Scaffold
Type V collagen is involved in the formation of cell surfaces and hair. It also plays a role in the production of the placenta in pregnant women. Supplements containing Type V collagen can support hair health and strength, contributing to overall hair vitality and growth.

In Conclusion
Understanding the different types of collagen and their specific benefits allows individuals to choose supplements and dietary sources that best meet their health and beauty goals. Whether it’s enhancing skin elasticity, supporting joint health, or ensuring the strength of bones and muscles, incorporating the right types of collagen into your diet can play a significant role in maintaining overall wellness.